Recently, Professor Jiang Jun and Associate Professor Xie Peng from the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering have made new progress in the field of Catalytic Asymmetric P−H Insertion Reactions. In their research, they developed a catalytic asymmetric system using copper catalysts and chiral quinoline amides. This provides a highly stereo-selective synthetic method for constructing structurally diverse chiral organophosphorus compounds and offers a viable approach to developing efficient catalytic asymmetric systems for carbene reactions. The related research findings have been published in the international academic journal the American Chemical Society (2023, DOI: org/10.1021/jacs.3c06906) titled Catalytic Asymmetric P−H Insertion Reactions.
Organophosphorus compounds are widely applied in the fields of organic chemistry, medicinal chemistry, and materials science. The high stereo-selective construction of chiral organophosphorus compounds is a crucial research direction in the field of organic chemistry. The P-H insertion reaction of metal carbenes provides a rapid and efficient synthetic method for building C-P bonds. However, after over three decades of development, the challenge of achieving asymmetric catalysis in P-H insertion reactions has remained unresolved. To solve this problem, Jiang and Xie’s team proposed a strategy involving the co-catalysis of copper metal and chiral quinoline amides. They have developed an asymmetric catalytic P-H insertion reaction of diazoacetamides with phosphine hydrides. This breakthrough enables precise control over the stereo-selectivity of the proton transfer process, elucidates the asymmetric catalytic mechanism of P-H insertion reactions, and allows for the highly chemically and stereo-selective synthesis of a diverse range of chiral β-hydroxyphosphine oxide compounds.
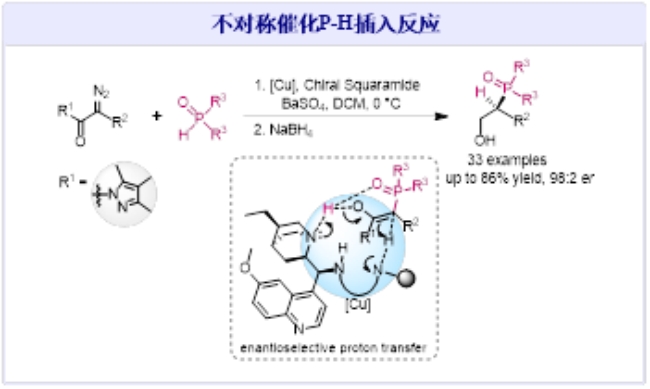
The first author of the paper is Gu Xiu, a doctoral student from the School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Class of 2019. The corresponding authors are Associate Professor Xie Peng and Professor Jiang Jun, and Guangxi University is the sole corresponding institution for this paper. This paper represents a significant breakthrough in the previous research on metal carbene P-H insertion reactions. In pursuit of efficient synthesis involving C-P bonds, Professor Jiang’s research team conducted systematic and in-depth investigations, resulting in a series of research advancements:
They achieved high stereo-selective P-H insertion reactions through a chiral induction strategy, providing an efficient asymmetric synthetic pathway for chiral phosphorus center phosphine oxide indole derivatives. This research was published in Organic Letters (2017, 19, 782).
Through nickel-catalyzed reactions, they unexpectedly discovered a new reaction pathway at the 1,2-position of heteroallenes, elucidating the catalytic process involving nickel complexed enone imine intermediates. This research was published in Organic Letters (2019, 21, 4944).
To effectively address the challenge of α-alkyl metal carbene α-H migration, they developed a Rh(I)-catalyzed strategy that efficiently suppresses α-hydrogen migration and elucidated the underlying mechanism responsible for its excellent catalytic performance. This research was published in Chemical Science (2017, 8, 4312).
They developed a green synthesis method for constructing C-P bonds through visible-light-catalyzed P-H insertion reactions with free carbenes. This research was published in Organic Letters (2023, 25, 2338).
By employing gold catalysis in the isomerization/reduction/addition reaction of ortho-nitroalkynes with phosphine hydrides, they developed a direct synthesis method for N-unsubstituted phosphinoyl indolin-3-one skeletons without the need for external reducing agents. This research was published in Chemical Communications (2022, 58, 8568).
They achieved asymmetric hydrogenation of the intermediate methylphenylquinone using chiral organic small molecule catalysts, resulting in high stereo-selective hydrogenation reactions of ortho-methylphenylquinone. These research findings were published in "Organic Letters" (2018, 20, 7229) and Organic Chemistry Frontiers (2021, 8, 2002).
The research on catalytic asymmetric P-H insertion reactions was supported by various sources, including the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation, and the Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education.